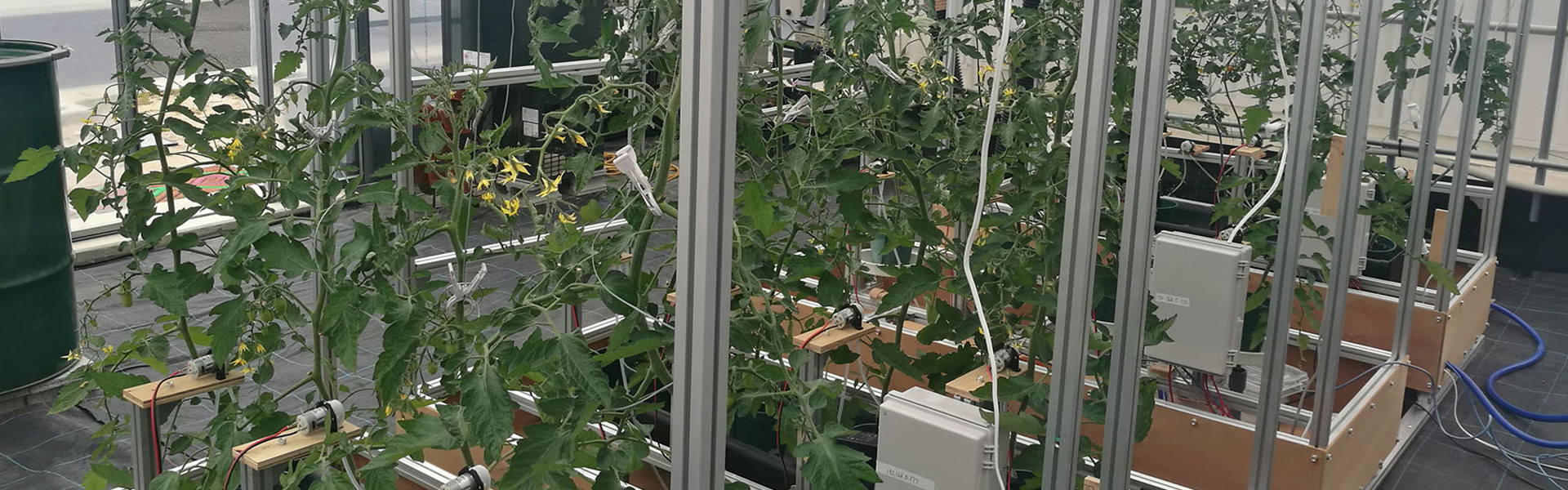
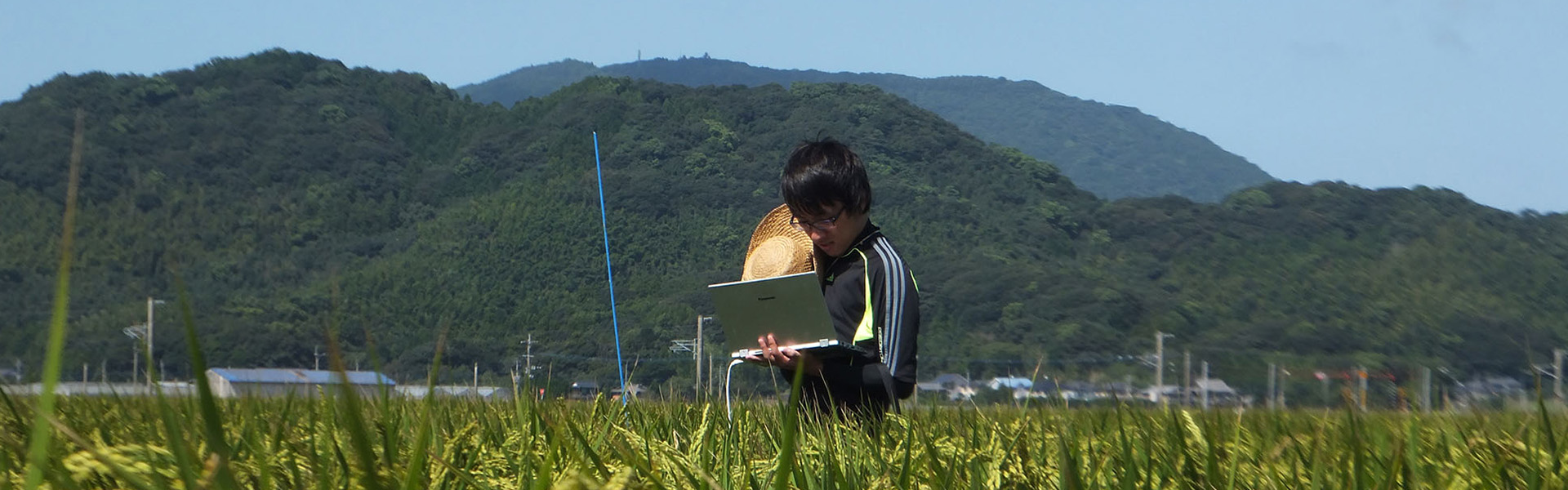
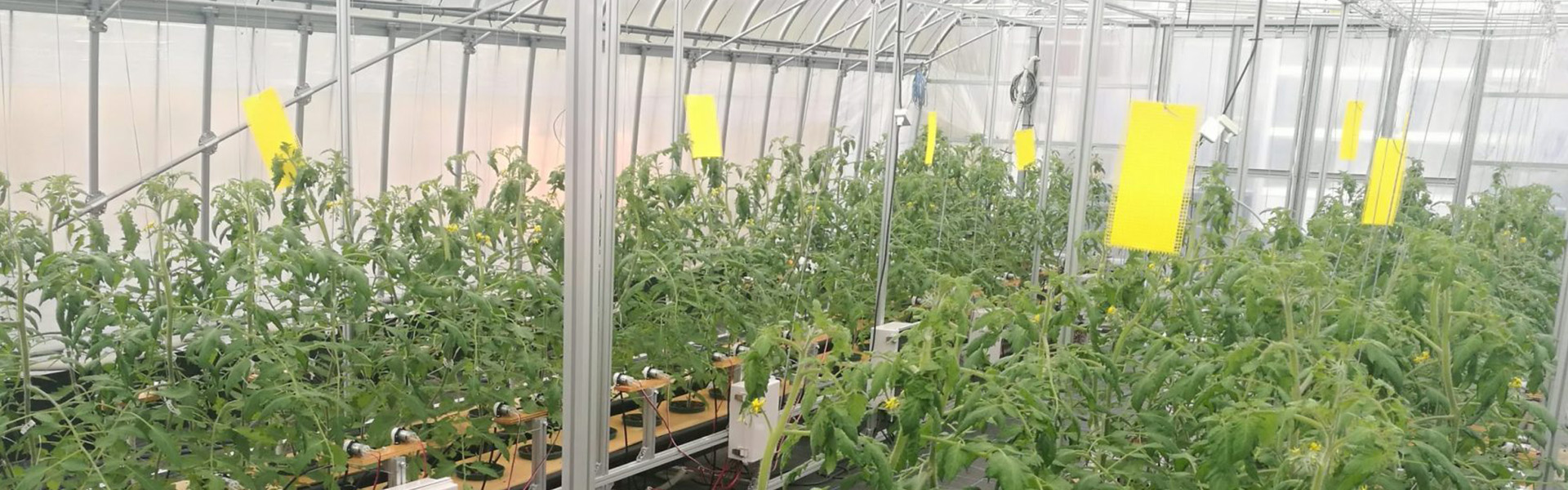
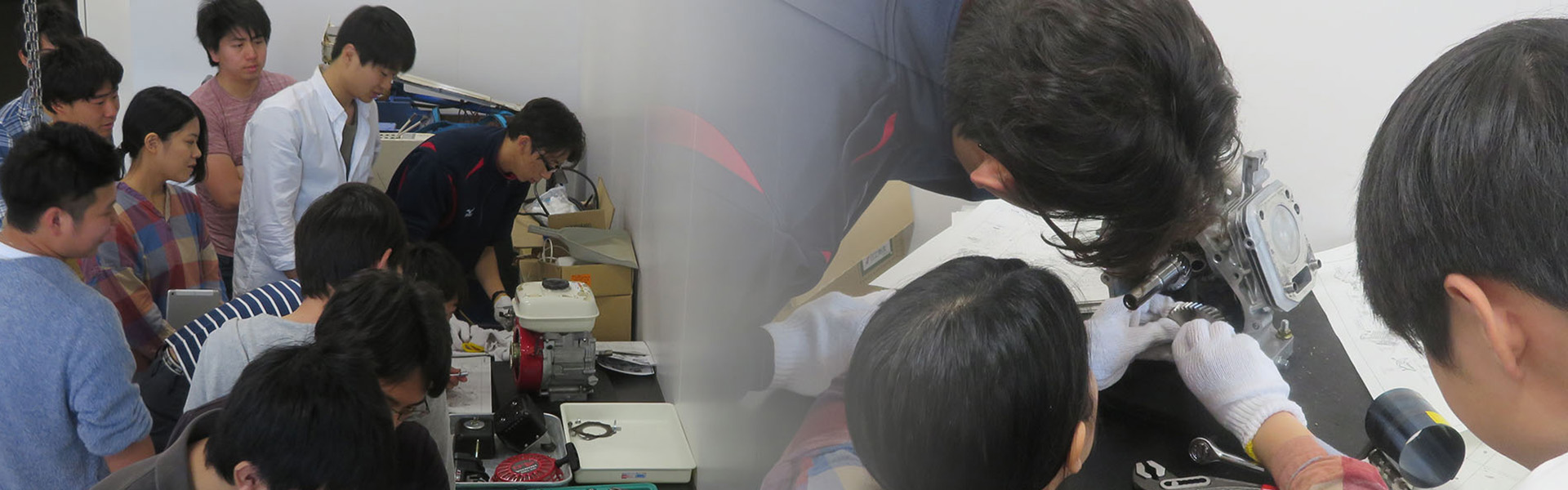
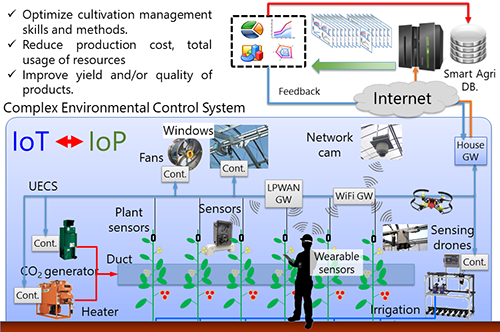
Agricultural production strongly depends on climate, weather, soil properties, plant type, and so on. Thus, farmers have tried to continuously modified cultivation strategy and techniques for a long time so as to fit the ambient environmental and plant conditions. Additionally, consumers’ demands have also shifted to fresh, high-quality, and high-security fruits and vegetables. In response to these issues, various researches and developments have been investigated to establish next generation of agriculture up to now. The core technology will be Information and Communication Technologies (ICT). Currently, there are a lot of ICT applications in agriculture (smart farming) including a spatio temporal data collection and a facility automation including environmental monitoring and control in a greenhouse. Various affordable devices such as low-price microcomputers and sensors and open source software are developed year by year, and then these advents have completely changed the environment and views for the utilization of ICT in agriculture. We are also developing several technologies to improve agricultural production using affordable devices and open source software for small and medium-scale farms.